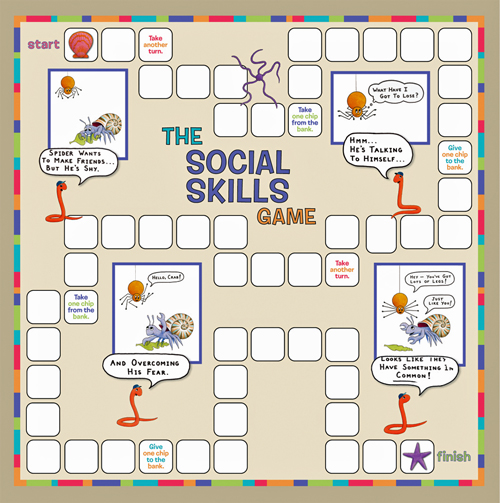
This skill-building board game teaches children attitudes and behaviors that promote positive social interactions.
Game cards focus on four skill areas: Making Friends, Responding Positively to Peers, Cooperating with Peers, and Communicating Needs.
Included in the game manual are three inventories that can be used to identify the child’s specific skill deficits. Can be played by one or more students with an educator or parent.
Skills Covered
The game addresses 20 specific behaviors, which fall into four social skill categories:
Making Friends
- Asking questions
- Giving compliments
- Introducing oneself
- Listening
- Starting conversations
Cooperating With Peers
- Following rules
- Joining in
- Sharing
- Suggesting activities
- Taking turns
Responding Positively to Peers
- Accepting compliments
- Helping peers in trouble
- Offering help
- Showing concern for peers
- Standing up for peers
Communicating Needs
- Asking for help
- Asking to borrow others’ property
- Expressing negative feelings
- Expressing positive feelings
- Getting attention appropriately
The game also teaches the six cognitive skills and orientations that improve social interactions:
Self-Reinforcement (SR)
Socially competent behavior is likely to be repeated if the child compliments or rewards himself or herself for it.
Causal Attribution (CA)
Socially competent behavior is likely to be repeated if the child attributes success to his or her own effort and/or ability rather than to chance or others’ behavior.
Performance Mediation With Anxiety (PMA)
Socially competent behavior is more likely if the child can learn to cope with the anxiety that is often associated with social interaction.
Performance Mediation With Mistakes (PMM)
Socially competent behavior is more likely if the child can learn to focus on the successful components of imperfect social interactions.
Expectations of Efficacy (EXE)
Socially competent behavior is more likely if the child feels capable of performing the behavior.
Expectations of Outcome (EXO)
Socially competent behavior is more likely if the child feels that it will lead to desirable outcomes.